Charles Plosser, CEO of Philadelphia’s Federal Reserve, addressed an audience at Cato Institute on the topic of employing monetary policy to prevent asset bubbles, which caused the current recession. He told the audience that using monetary policy to adjust interest rates in order to compensate for asset price gaps (bubbles) was not a good idea. One example given was raising rate on mortgages to restrict rising housing prices. Two reasons for being against employing broad-based monetary policy for individual asset markets like housing were: (1) The risk of wrecking havoc in other parts of the economy is too great, and (2) no precise measure of asset-movement exists by which to form sound rule-based monetary policy. (Read his Cato speech titled “Bubble, Bubble, Toil and Trouble: A Dangerous Brew for Monetary Policy.)
John Mauldin, CEO of Millenium Wave Advisers, came to a similar conclusion about Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke’s decision to inflate the economy through the latest $600 billion quantitative easing. Bernake’s reason was to prevent deflation, which means core inflation rate as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) dropped below 1 percent. Core inflation is all consumer goods except food and energy. Mauldin claims core inflation is actually about 1.5% not 0.6% when housing costs are removed.
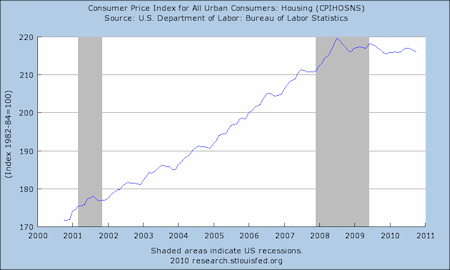
There seems to be two reasons Mauldin measures inflation without housing costs: (1) Historically, the Bernanke should have used monetary policy to lower an increasingly high inflation rate back in 2005 that was caused by the housing price bubble. (2) More important is the fact that over the past few years housing cost is growing at near zero percent (see the chart below).
If Puru Saxena, CEO of Hong Kong based Puru Saxena Wealth Management, is right, Bernake’s quantitative easing will not revive the U.S. economy. Just like the previous two stimulus bailouts, quantitative easings never do. (Read his article titled “Band-Aid Solutions”
What Bernanke’s cash infusion will do is devalue the dollar. This will causing food, energy, and everything else to rise, which will act as a tax on disposable income. Less disposable means fewer sales. As Mauldin also pointed out, food and energy costs already are high for those with lower income. These people will suffer the most as a result of the Fed’s easy quantitative induced inflation.
There are some creative ideas that could solve the housing price problem. For example, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and FHA could rent their growing stock of foreclosed houses, which would keep some people in their homes. Banks also could lend to investors (landlords) to buy cheap housing if they promise to rent them out. Read Maudlin’s article “O Deflation, Where is Thy Sting?” to learn more.