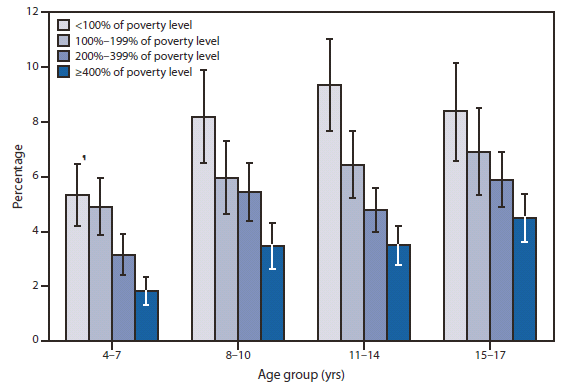
During 2004-2009, approximately 5.1% of all U.S. children aged 4-17 years were reported by parents as having serious emotional or behavioral difficulties. Across all age groups, poor children (i.e., those living in families with incomes <100% of the poverty level) more often were reported to have serious emotional or behavioral difficulties compared with the most affluent children (i.e., those living in families with incomes ?400% of the poverty level). For example, among children aged 11–14 years, approximately 9.3% of poor children were reported by parents to have serious difficulties, compared with 3.5% of the most affluent children. (CDC, May 6, 2011)
Supporting the statistics above is research published in the American Journal of Preventative Medicine. The multi-author report titled “Effectiveness of Universal School-Based Programs to Prevent Violent and Aggressive Behavior” stated the following:
“Over the last 25 years, youths aged 10 to 17 years, who constitute less than 12% of the population, have been involved as offenders in approximately 25% of serious violent victimizations.[3] Homicide and suicide, respectively, are the fourth and fifth leading causes of death among children aged 5 to 14 years, and the second and third leading causes of death among people aged 15 to 24 years.[4]
“Risk factors for youth violence include low socioeconomic status (SES), poor parental supervision, harsh and erratic discipline, and delinquent peers.[5] Delinquent youths commonly have other problems as well,[6] including drug abuse, difficulties at school, and mental health problems (as indicated by being in the top 10% of the distribution of externalizing and internalizing symptoms in the Child Behavior Checklist[7]). These youths are threats not only for the direct harm they may cause, but also because they may play roles in the socialization of other potential delinquents.[8]”
Yet, the Columbine High School massacre was perpetrated by youth from upper-middle class backgrounds. So were many other youth who killed their peers. The same was true of those Arab-Muslims who perpetrated the 9-11 attack. Growing up in a violent drug culture will obviously influence a child’s emotions and behavior and school programs may help prevent some children from succumbing to it. However, it is parents, relatives and close family friends who have the strongest influence.
If society would reform the political economy for the common good, most poor families would no longer be poor. Emotional and/or behavioral problems resulting from financially induced stress of many parents would wane. The emotional and behavioral problems of many children would subside as well. Even though economic status is not really the answer to those problems, alleviating stress related issues is at least part of the solution.
Liberals seem to see welfare socialism as the needed reform, and conservatives see less government bureaucracy that comes with welfare and more free market initiatives as the appropriate reform. It is doubtful that either have the right solution.